Migrating sensitive data and mission-critical workloads to the AWS cloud can pose significant challenges, particularly in terms of security, reliability, and performance. One of our clients faced this exact dilemma, with terabytes of customer data and complex applications residing on their on-premises servers. Security and compliance were paramount concerns, as any disruptions during migration could lead to severe consequences. They needed a solution that would ensure security, reliability, and compliance.
After evaluating various AWS services, we determined that AWS Direct Connect was the perfect fit for our client’s migration needs. It offers enhanced security, cost efficiency, and robust performance, aligning seamlessly with their migration objectives. In this blog, we’ll delve into how AWS Direct Connect facilitates a seamless and secure migration.
What is AWS Direct Connect?
In the vast expanse of cloud computing, establishing robust and reliable connectivity between on-premises infrastructure and cloud services is fundamental. AWS Direct Connect, a pioneering solution offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS), serves as a dedicated highway, enabling organizations to seamlessly bridge their on-premises environments with the vast ecosystem of AWS cloud services.

Why did we Choose AWS Direct Connect inspite of other AWS services?
1. AWS Site-to-Site VPN: Site-to-Site VPN provides encrypted connectivity between your on-premises network and AWS VPCs over the public internet. While VPNs offer flexibility and ease of setup, they may not match the performance and security guarantees of Direct Connect, especially for latency-sensitive or bandwidth-intensive workloads.
2. AWS VPC Peering: VPC Peering allows direct connectivity between VPCs within the same AWS Region or across different Regions. While Peering is suitable for intra-cloud communication, it lacks the dedicated, high-performance characteristics of Direct Connect, making it less suitable for large-scale migrations or real-time applications.
3. AWS Transit Gateway: Transit Gateway simplifies network connectivity by acting as a hub for connecting multiple VPCs, VPNs, and Direct Connect connections. While Transit Gateway offers scalability and centralized management, it complements Direct Connect rather than serving as a direct replacement, as Direct Connect provides dedicated, private connectivity.
[Good Read:Top 5 DevSecOps Trends In 2024 ]
Key features and Components of AWS Direct Connect
- Dedicated Connection: Ensures reliable network performance compared to internet-based connections.
- Virtual Interfaces: Allows connection to various AWS services or regions over a single physical connection.
- Redundancy: Facilitates high availability and fault tolerance through redundant connections.
- Connection Speeds: Supports speeds ranging from 50 Mbps to 100 Gbps, based on requirements.
- Global Reach: Available in various AWS regions globally, enabling connectivity across regions.
- AWS Direct Connect Gateway: Connects multiple VPCs in different regions to on-premises networks.
- Private Connectivity: Ideal for scenarios requiring enhanced security and dedicated network performance.
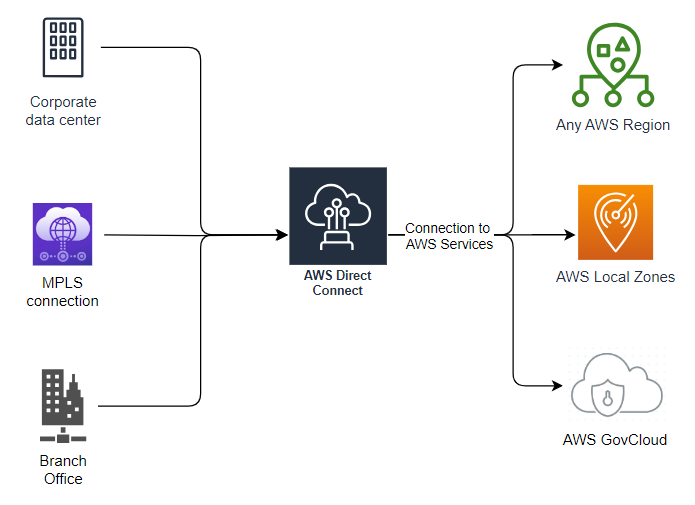
Essential Steps and Decisions for On-Premises Connectivity
When you implement Direct Connect, you have several decisions to make before you can log into the console and create a connection from the Direct Connect dashboard.
The choices made at each step will make a complete picture of the requirements you need to meet to successfully connect to your AWS environment. First, note that Direct Connect only supports 802 .1Q encapsulation.
All equipment that will be a part of the physical connection linking to your location with AWS must support 802 .1Q encapsulation.
Three Ways to implement AWS Direct Connect
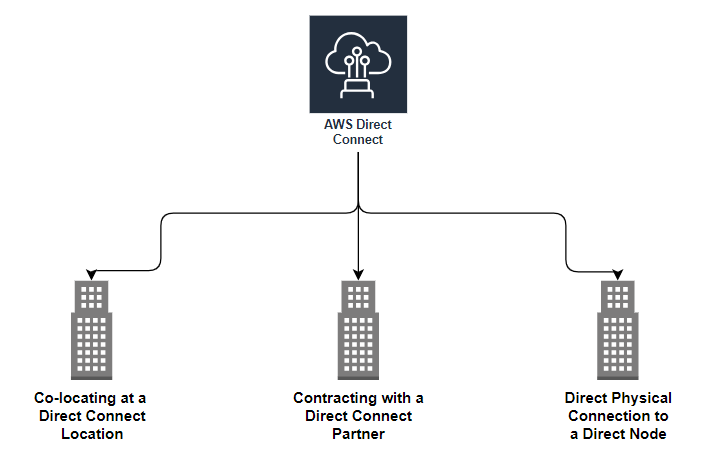
1. Co-locating at a Direct Connect location
AWS has partnered with companies around the world to offer physical uplinks to AWS through the Direct Connect service. Typically, you select a Direct Connect location best suited for your needs by talking with the Direct Connect partners near you.
When you have selected the Direct Connect location, you deploy a router and supporting equipment to that location. The equipment you deploy will be the physical connection between your on-premises location and the AWS router at the Direct Connect location.
By this way, you are responsible for three things, the deployed equipment, the circuit that will connect your on-premises location to the deployed equipment, and the connection from the deployed equipment to the AWS router.
2. Contracting with a Direct Connect Partner
The second option is to contract with a Direct Connect partner who already has equipment at the Direct Connect location. If you choose this option, the Direct Connect partner will provide you with the necessary equipment at the Direct Connect location that will connect to the AWS router.
In most cases, you will need to provide the physical connection between your on-premises location and the Direct Connect Partner equipment, but the Direct Connect Partner will configure and maintain the physical equipment at the Direct Connect location.
3. Direct Physical Connection to a Direct Connect Node
The third and final option is to reach an agreement with AWS to make a direct physical connection from your on-premises location to a Direct Connect node. When you do this, you are responsible for all of the equipment from the node to your location.
You can check more info about-
Comments
Post a Comment